SOIL SCIENCE 109
Midterm One
Spring 1997
(10 points)
1. Define the relationship between nutrient uptake and plant growth by illustrating on a graph the stages of nutrient uptake through the growing season for an annual crop.
(5 points)
2. (a) Define the fundamental difference in the interpretation of the "law of the minimum" as described by Liebig and Mitscherlich.
(10 points)
2. (b) Illustrate on a graph Mitscherlich’s concept as discussed in class where a limiting nutrient is essential (added nutrient causes increase in yield), the critical concentration (point of no economic return), and toxic level. Label axis with appropriate legends.
(6 points)
3. (a) List the criteria for an essential element.
(8 points)
3. (b) List four essential macro- and four essential micronutrients and briefly describe one of its most important function.
(6 points)
4. (a) List three mobile and three nonmobile nutrients inside a plant.
(5 points)
4. (b) Describe in general terms of leaf age the symtoms of nutrient deficiency of mobile and nonmobile nutrients.
(4 points)
5. (a) We spent a lot of time discussing factors which regulate the composition of the soil solution. Why is the soil solution phase important?
(6 points)
5. (b) List three factors that regulate the composition of the soil solution.
(10 points)
6. Describe the extractants used in in the determination of cation exchange capacity, why those particular extractants are used, and what can be measured in the different extractant solutions.
(10 points)
7. Complete the following reaction.
| H+
| + CaCO3®
| H+
(10 points)
8. Calculate the calcium carbonate equivalent of blast furnace slag (CaSiO3).
Molecular weight of: CaCO3 = 100 and CCE = 100
CaSiO3 = 116
(5 points)
9. (a) What type of interaction is displayed in the following graph?
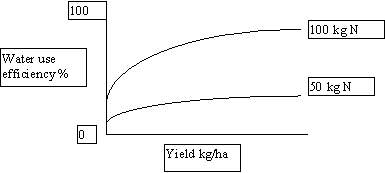
(5 points)
9. (b) Describe the reason for the increase in water use efficiency caused by the addition of additional N in the above graph.
