Soil Science 100
Second midquarter examination
Answer Key
Friday November 15, 2001
Value 100 points
|
Please answer all questions in the space provided. Please put your name on one of the pages after the first page. |
|||
|
1. |
a |
(8) |
What are the four components of head that make up the total head when considering water flow in soil? gravity, pressure, osmotic (solute) and matric |
|
|
b |
(8) |
For each of the head components, state whether it is included or ignored when calculating saturated flow and unsaturated flow in soil (for example, head x is included in saturated flow but not included in calculating unsaturated flow). |
|
Head component |
Saturated |
Unsaturated |
|
Gravity |
included |
included |
|
Pressure |
included |
ignored |
|
Solute |
ignored |
ignored |
|
Matric |
ignored |
included |
|
|
c |
(9) |
For any head component that you state is “unimportant or ignored” in the calculation, briefly explain your answer. The pressure component is ignored
in unsaturated flow because the water is considered to be at atmospheric
pressure (the standard state) whenever the soil is unsaturated. The solute or osmotic component is
typically ignored when calculating flow because soil rarely has an uneven
distribution of salt that would produce an osmotic component. The matric component is ignored in
saturated flow because at saturation the majority of water flow is far from
surfaces and unaffected by surface attraction. |
|
2. |
|
(10) |
List five factors that influence the rate of microbial decay of soil organic matter. Size, composition or the organic matter (its quality according to the text). Density and porosity of the organic matter. Soil pH, clay content, clay type, water content, oxygen content, temperature are all factors that influence decay rates. (two points each) Use your judgement on correct or not if not in my list. |
|
3. |
|
(6) |
What are the two most important characteristics of ions in soil solution that determine the strength of their interaction with the soil exchange complex? The size and charge of the ion. |
|
4. |
|
|
Why do wet soils warm more slowly in the spring than dry soils? Wet soils have a higher heat
capacity than dry soils and therefore require more heat to raise their
temperature. Energy goes into
evaporation of the water, reducing the amount of energy that heats the soil. |
|
5. |
a |
(6) |
What are the two mechanisms by which heat may flow in soil? Conduction and convection (mass
flow) |
|
|
b |
(6) |
Which is most important and why? Conduction is most important
because the flow of air in pores is very slow. Still air is a good insulator. |
|
6. |
|
(10) |
Draw a graph that shows the soil water content as a function of total potential over a wide range of water content for a sandy texture and a clay texture. Label the two axes and each curve fully. (one point for each correct label and for the curves to be correct.) |
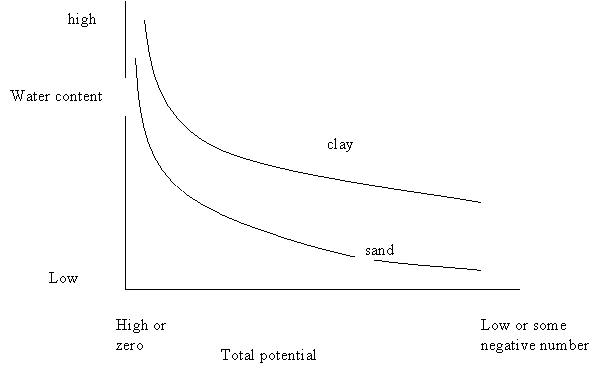
|
7. |
|
|
Soil organisms require four conditions for successful
growth. |
|
|
a |
(8) |
What are these four conditions? Sufficient space, water, and
nutrients and satisfactory temperature. |
|
|
b |
(12) |
For each of these, comment on how A horizons and C horizons differ (in general) in providing these conditions. I have four responses, one for each factor. Give three points for each. If there are other correct answers, give up to three points for each up to a total of 12. Both A and C horizons will provide sufficient space (pores and surfaces for microorganisms). A horizons are likely to have much more variable moisture conditions than C horizons but are also likely to provide better conditions for those organisms that require wetness to proliferate. Nutrients, especially carbon and nitrogen are likely to be more abundant in A than C horizons. A horizons will have a much more
variable temperature regime for organisms than will C horizons. |
|
8. |
|
(6) |
Explain the difference in energy sources used by soil microorganisms that are heterotrophs compared to those that are autotrophs. Heterotrophs require organic carbon
in a form that they can utilize while autotrophs use sunlight
(photoautotrophs) or oxidation of inorganic compounds (lithoautotrophs or
chemoautotrophs) for energy. |
|
9. |
|
(6) |
You took a 5 mL aliquot of an original extract and diluted it to a volume of 50 mL before determining the N concentration. The N concentration of the diluted soil extract was 1.5 mg/mL. If 20 g of oven dry soil was extracted with 100 mL, what was the N concentration in one gram of the oven-dry soil? Give 1 point for the correct numerical answer and 1 point for the correct final units. Give four points if the problem is correctly set up (with or without units). 1.5 mg/mL * 50mL/5mL * 100 mL/20g = 75 mg/g |